Understanding E&M Codes Guide
What are E&M Codes?
Evaluation and management codes, often referred to as E&M codes or E and M codes are a coding system that involve the use of CPT codes from the range 99202 to 99499 which represent services provided by a physician or other qualified healthcare professional. These evaluation and management CPT codes are utilized when the provider is involved in either evaluating or managing patient health. These E&M CPT codes are commonly used by specialty care consultants, emergency room physicians and primary care physicians. For example, office visits, hospital visits, home services and preventive medicine services are considered E&M codes. Codes for procedures like surgeries, radiology and diagnostic tests, and certain treatment therapies are not considered evaluation and management services.
E&M codes are used to represent the various physician and provider services primarily centered around the evaluation and management of patients. E&M coding is not about procedures or tests but rather focuses on the cognitive services provided by healthcare professionals, such as patient consultations, physical examinations, and medical decision-making processes.
The Significance of E&M Coding in Healthcare
The utilization of E&M codes is a fundamental aspect of medical billing. These codes determine the reimbursement level for the time and effort spent by healthcare professionals in assessing and managing a patient's care. Inaccurate or inappropriate E&M coding can lead to either underbilling, which means a loss of revenue for the healthcare provider, or overbilling, which can result in audits, fines, and even legal action.
E&M Coding Guidelines
To ensure accuracy and compliance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the AMA have established detailed E&M coding guidelines. These guidelines provide a framework for selecting the correct E&M code based on various factors such as the complexity of the medical decision-making, the intensity of the evaluation, and the setting in which the service is provided (such as a hospital, outpatient clinic, or private office).
Evaluation and Management Guidelines: Complexity and Setting
The evaluation and management guidelines categorize E&M services based on the complexity of patient care. The codes are divided into levels that reflect the intensity of medical decision-making – from straightforward to highly complex cases. Additionally, the setting where care is provided plays a significant role in code selection. For instance, different codes are used for services provided in a hospital compared to those in an outpatient setting.
EM Coding Guidelines: Documentation
Proper documentation is the cornerstone of E&M coding. The EM coding guidelines emphasize the importance of detailed and accurate medical records. Physicians and healthcare providers must document the patient's history, examination findings, and decision-making processes in a manner that justifies the E&M code selected. This documentation not only supports billing but also ensures continuity of care.
E&M Services: Breadth and Scope
E&M services encompass a wide range of patient interactions. These services include, but are not limited to, routine office visits for chronic conditions, hospital follow-ups, emergency department visits, and complex consultations for new or acute problems. Each type of interaction has specific coding requirements that reflect the service's complexity and the provider's effort.
E/M Medical Abbreviation: Understanding its Broad Application
The E/M medical abbreviation is broadly applied in healthcare to denote 'evaluation and management'. This term signifies the essence of these codes – they are not about a specific procedure or test but about assessing a patient's health status and managing their care. E/M coding is central to primary care and specialties that rely heavily on cognitive services rather than procedural interventions.
E/M Codes: The Building Blocks of Medical Billing
E/M codes are the building blocks of medical billing in outpatient and hospital settings. They are the most frequently used codes and significantly impact healthcare providers' revenue cycle management. Accurate E/M coding ensures that providers are fairly compensated for the time and complexity involved in patient care.
E/M Meaning in the Context of Patient Care
In the context of patient care, E/M meaning goes beyond coding and billing. It reflects the quality and depth of healthcare services provided. Proper use of E&M codes ensures that patient care is appropriately documented and reimbursed, which in turn supports the sustainability of healthcare practices and the overall healthcare system.
E&M Coding Cheat Sheet
E&M codes are organized into the following subcategories:
(99201–99215) Office/other outpatient services
(99217–99220) Hospital observation services
(99221–99239) Hospital Inpatient services
(99241–99255) Consultations
(99281–99288) Emergency department services
(99291–99292) Critical care services
(99304–99318) Nursing facility services
(99324–99337) Domiciliary, rest home (boarding home) or custodial care services
(99339–99340) Domiciliary, rest home (assisted living), or home care plan oversight services
(99341–99350) Home health services
(99354–99360) Prolonged services
(99363–99368) Case management services
(99374–99380) Care plan oversight services
(99381–99429) Preventive medicine services
(99441–99444) Non face-to-face office visits
(99450–99456) Special evaluation and management services
(99460–99465) Newborn care services
(99466–99480) Inpatient neonatal intensive, and pediatric/neonatal critical care services
(99487–99489) Complex chronic care coordination services
(99495–99496) Transitional care management services
(99499) Other evaluation and management services
Important Guidelines for E&M CPT Codes
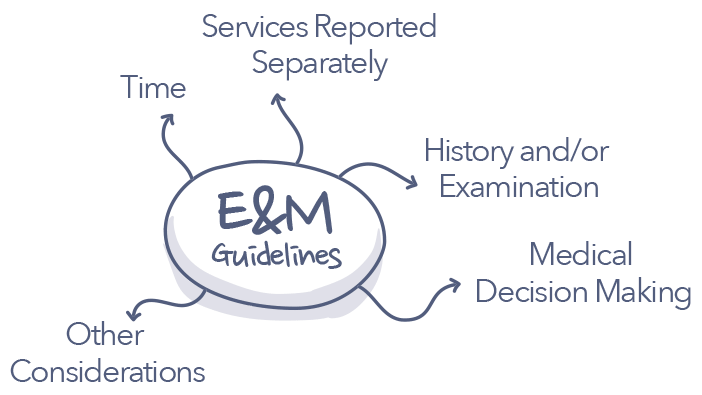
Physicians use E&M CPT codes to bill for services and obtain reimbursement. The AMA is responsible for creating the evaluation and management codes and the guidelines for how those codes are utilized. Physicians and coders must understand the guidelines so that they can accurately select the appropriate E&M codes for the service. Below are some important considerations to better understand the guidelines for selecting the appropriate evaluation and management codes.
Time
The amount of time or the total time of the encounter on the date of the encounter determines the appropriate evaluation and management CPT codes. This can include face-to-face and non-face-to-face time personally spent by the physician and includes the following items:
Preparing to see the patient (e.g., review of tests)
Obtaining and/or reviewing separately obtained history
Performing a medically appropriate examination and/or evaluation
Counseling and educating the patient/family/caregiver
Ordering medications, tests, or procedures
Referring and communicating with other health care professionals (when not separately reported)
Documenting clinical information in the electronic or other health record
Independently interpreting results (not separately reported) and communicating results to the patient/ family/caregiver
Care coordination (not separately reported)
It excludes any travel time, time spent on any procedure which is being billed separately, as well as teaching unrelated to that specific patient.
Services Reported Separately
Any additional procedure performed during the same encounter with a specific procedure code should be reported separately. For example, any diagnostic tests performed or interpreted and billed separately should not be included in determining the amount of time utilized when determining the appropriate evaluation and management CPT codes.
History and/or Examination
The nature and extent of the history and/or physical examination are determined by the treating physician, and it should be medically appropriate. However, the extent of the physical examination is not an element in selection of the level of office or other outpatient codes.
Medical Decision Making (MDM)
The number and complexity of the problems that are addressed at an encounter
The amount of data to be analyzed. Data can include medical records, tests, and other information that can be reviewed during or for the encounter
Tests, documents, orders, or independent medical histories
Independent interpretation of tests
The risk of complications due to the morbidity or mortality of patient management decisions made at the visit associated with the patient’s problem, diagnosis, or treatment
Four types of MDM are recognized: straightforward, low, moderate, and high, AMA has a table with guidelines that can be accessed here
Other Considerations
New or established patient
Prolonged services are codes for when a physician provides direct patient contact that is provided beyond the usual service either in the inpatient or outpatient setting. A different set of codes are used for prolonged services without direct patient contact.
E&M Codes and CMS Reimbursement Trends
CMS is the most important payor in the United States and how CMS sets its reimbursement schedules for healthcare services is an important determinant in reimbursement trends for private and public insurance companies and health plans.
In the past twenty years or so and even as recently as 2020, CMS has improved reimbursement for evaluation and management CPT codes. The counter trend is that reimbursement for procedures like surgeries and related specialties are being lowered. For example, endocrinologists, rheumatologists, hematologists/oncologists, family physicians and psychiatrists have seen reimbursement increases over the past few years. Conversely, radiologists, cardiac surgeons, anesthesiologists, critical care physicians and general surgeons are among those types of physicians projected to see the largest drops in Medicare reimbursement. Many other types of specialists will see drops as well.
Evaluation and Management Key Takeaways
E&M CPT codes are a vital component of healthcare billing and coding. Understanding what are E&M codes, adhering to E&M coding guidelines, and appreciating the nuances of evaluation and management guidelines are essential for accurate and efficient healthcare billing. E&M services represent a significant part of patient care, and the correct application of E/M codes ensures that this care is accurately captured and reimbursed.
If you are an office-based physician, you should really spend the time understanding the coding guidelines for evaluation and management services. Inaccurate or incorrect billing can lead to criminal and/or civil penalties. Knowingly submitting false claims to obtain a federal health care payment for which no entitlement would otherwise exist is considered Medicare fraud. Misusing codes on a claim, such as up-coding or unbundling codes is considered Medicare abuse. Reimbursement trends from CMS tend to favor E&M codes and those physicians that use those codes frequently in their practice. The AMA, CMS and AAPC (American Association of Professional Coders) provide excellent resources and learning tools for CME, CE and self-education. As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of E&M coding remains central, underscoring the importance of these codes in the broader landscape of healthcare administration.
For healthcare organizations looking to succeed in the transformation to value-based care delivery models, including the Medicare Advantage Program, ForeSee Medical is a specialized software platform for accurate Medicare risk adjustment. Through artificial intelligence like proprietary medical algorithms and natural language processing, ForeSee Medical optimizes HCC coding, empowering providers to positively influence health outcomes.